FORECAST.ETS.STAT Function
The FORECAST.ETS.STAT function is one of the statistical functions. It is used to return a statistical value as a result of time series forecasting. Statistic type indicates which statistic is requested by this function.
Syntax
FORECAST.ETS.STAT(values, timeline, statistic_type, [seasonality], [data_completion], [aggregation])
The FORECAST.ETS.STAT function has the following arguments:
| Argument |
Description |
| values |
A range of the historical values for which you want to predict a new point. |
| timeline |
A range of date/time values that correspond to the historical values. The timeline range must be of the same size as the values range. Date/time values must have a constant step between them (although up to 30% of missing values can be processed as specified by the data_completion argument and duplicate values can be aggregated as specified by the aggregation argument). |
| statistic_type |
A numeric value between 1 and 8 that specifies which statistic will be returned. The possible values are listed in the table below. |
| seasonality |
A numeric value that specifies which method should be used to detect the seasonality. It is an optional argument. The possible values are listed in the table below. |
| data_completion |
A numeric value that specifies how to process the missing data points in the timeline data range. It is an optional argument. The possible values are listed in the table below. |
| aggregation |
A numeric value that specifies which function should be used to aggregate identical time values in the timeline data range. It is an optional argument. The possible values are listed in the table belows. |
The statistic_type argument can be one of the following:
| Numeric value |
Statistic |
| 1 |
Alpha parameter of ETS algorithm - the base value parameter. |
| 2 |
Beta parameter of ETS algorithm - the trend value parameter. |
| 3 |
Gamma parameter of ETS algorithm - the seasonality value parameter. |
| 4 |
MASE (mean absolute scaled error) metric - a measure of the accuracy of forecasts. |
| 5 |
SMAPE (symmetric mean absolute percentage error) metric - a measure of the accuracy based on percentage errors. |
| 6 |
MAE (mean absolute error) metric - a measure of the accuracy of forecasts. |
| 7 |
RMSE (root mean squared error) metric - a measure of the differences between predicted and observed values. |
| 8 |
Step size detected in the timeline. |
The seasonality argument can be one of the following:
| Numeric value |
Behavior |
| 1 or omitted |
Seasonality is detected automatically. Positive, whole numbers are used for the length of the seasonal pattern. |
| 0 |
No seasonality, the prediction will be linear. |
| an integer greater than or equal to 2 |
The specified number is used for the length of the seasonal pattern. |
The data_completion argument can be one of the following:
| Numeric value |
Behavior |
| 1 or omitted |
Missing points are calculated as the average of the neighbouring points. |
| 0 |
Missing points are treated as zero values. |
The aggregation argument can be one of the following:
Notes
How to apply the FORECAST.ETS.STAT function.
Examples
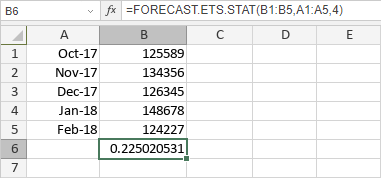
The figure below displays the result returned by the FORECAST.ETS.STAT function.
Return to previous page