- Home
- LOOKUP function
LOOKUP function
The LOOKUP function is one of the lookup and reference functions. It is used to return a value from a selected range (row or column containing the data in ascending order).
Syntax
LOOKUP(lookup_value, lookup_vector, [result_vector])
The LOOKUP function has the following arguments:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| lookup_value | A value to search for. |
| lookup_vector | A single row or column containing data sorted in ascending order. |
| result_vector | A single row or column of data that is the same size as the lookup_vector. |
Notes
The function searches for the lookup_value in the lookup_vector and returns the value from the same position in the result_vector.
If the lookup_value is smaller than all of the values in the lookup_vector, the function will return the #N/A error. If there is not a value that strictly matches the lookup_value, the function chooses the largest value in the lookup_vector that is less than or equal to the value.
How to apply the LOOKUP function.
Examples
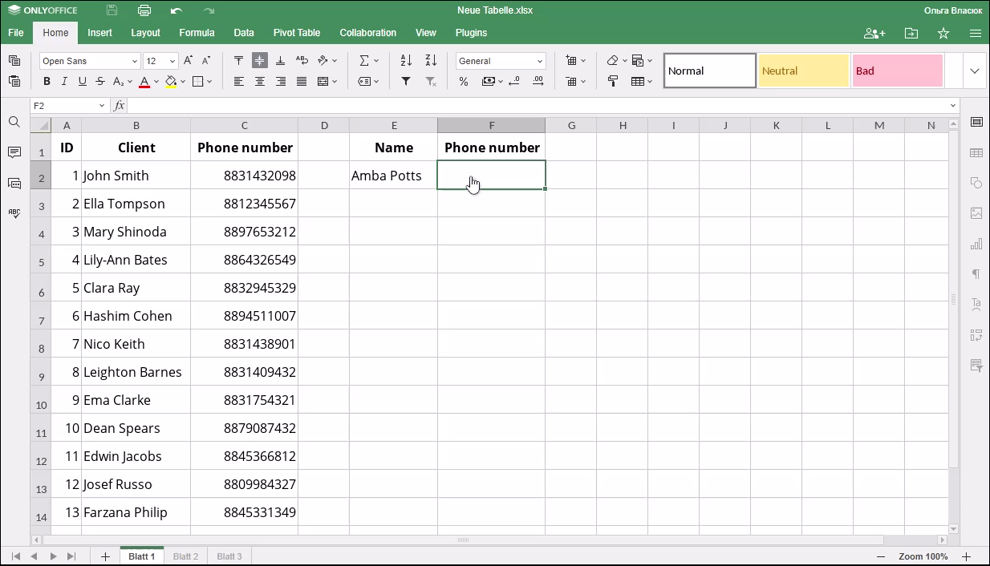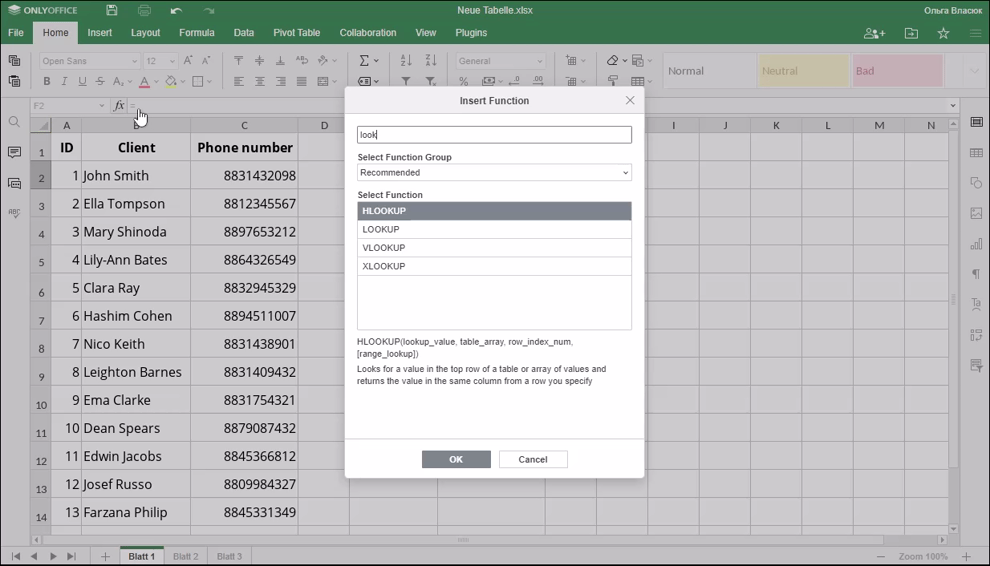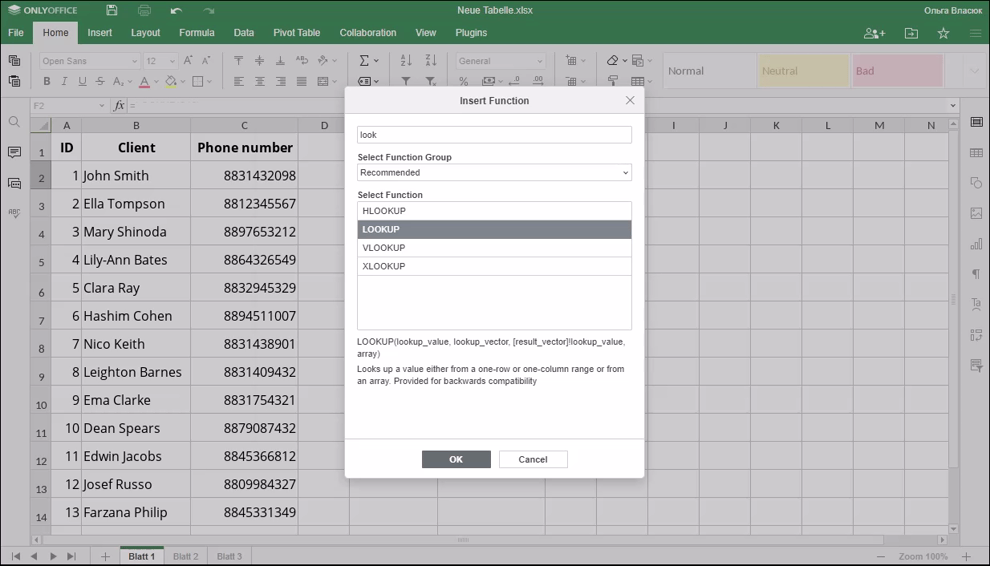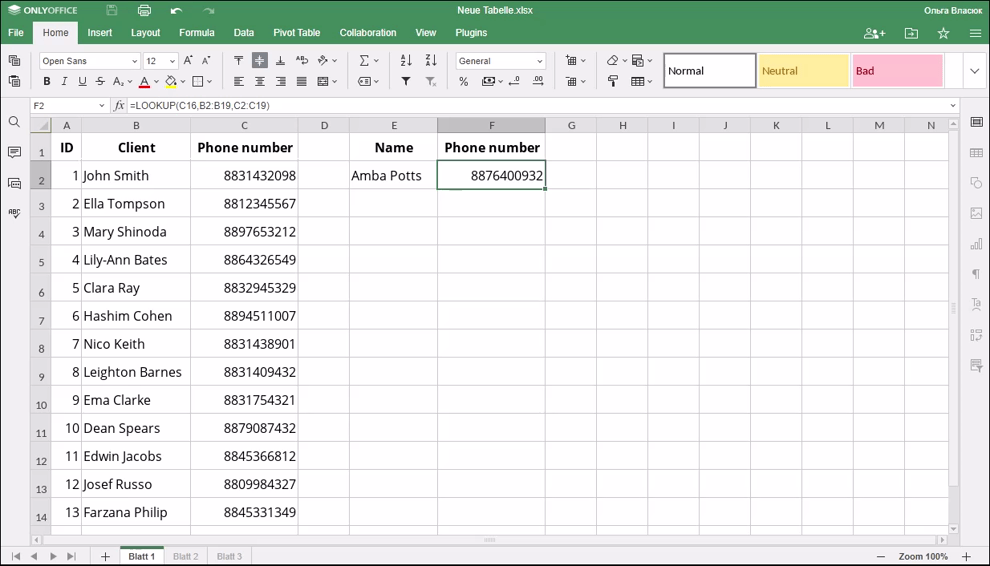
The figure below displays the result returned by the LOOKUP function.