ONLYOFFICE Mail is a tool that allows to work with email messages right on your portal. It provides a variety of the standard capabilities implemented in any other email client:
- connecting mailboxes,
- receiving and sending email messages,
- using the address book and managing contacts,
- setting up a signature,
- using the mail autoreply feature,
- printing messages.
Besides that, ONLYOFFICE Mail provides useful features that are not available when working with other email clients, namely it allows to add information to other entities on the portal, e.g. you can:
- automatically save documents from attachments into a shared folder on the portal,
- add new contacts into the CRM module,
- link the correspondence history with a CRM contact/opportunity/case,
- add events into the Calendar.
This is one of the portal tools used to create a single workspace and make your business communications and customer relationship more convenient and efficient. In addition to the above options, ONLYOFFICE Mail allows you to:
- send invoices to your customers right from the CRM system,
- attach any documents stored on the portal to email messages.
In the ONLYOFFICE Mail module, it's also possible to use ONLYOFFICE Mail Server that offers the following features:
- connect your domain,
- create corporate mailboxes,
- add aliases,
- create mail groups.
For a better understanding of the ONLYOFFICE Mail special characteristics and differences from other email clients like Thunderbird or MS Outlook, you should know what is email as a phenomenon and how the process of sending and receiving emails is performed in other email clients.
How do commonly used email clients work?
Email is a client/server solution. When sending and receiving email messages from an email client, the following client-side and server-side applications interact:
- MUA - Mail User Agent that allows to view incoming messages and transfers outgoing messages to the mail server,
- MTA - Mail Transfer Agent that transfers messages between servers,
- MDA - Mail Delivery Agent that receives incoming messages and delivers them to the recipient's mailbox.
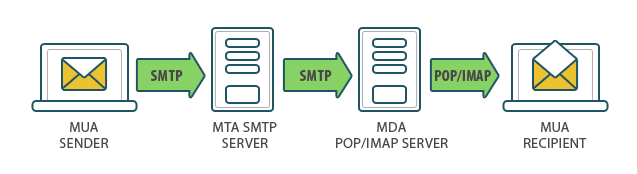
The process of sending messages from an email client is performed as follows:
- The sender transfers an email message from the email client to the mail server over the SMTP protocol.
- The sender's email client connects to its outgoing mail server.
- Once the connection with the mail server is established, the information about the email sender, recipient and the send date is transmitted to the server.
- The sender's mail server transfers the email message to the recipient's mail server over the SMTP protocol.
- The mail server queues the message. Before the message is actually sent, the server verifies if several conditions are performed.
- The sender's mail server refers to the Domain Name System (DNS) and verifies if the A and MX records exist for the domain specified in the recipient's email address.
- A record allows to obtain an external IP address associated with a domain name.
- MX record allows to find out where the mail server that receives mail for a domain is located.
- The sender's mail server verifies if port 25, which is responsible for the message delivery, is open on the recipient's incoming mail server.
- If all the requirements are met, the sender's mail server refers to the recipient's mail server, informs it about the intention to send the message and transfers the information about the email sender and certain recipient. If this recipient exists, the message body is sent.
- The recipient's mail server downloads the message and checks it for spam or viruses. If the message passes all checks, it is placed to the storage. If the message does not pass a check, it can be rejected.
- The recipient connects to his mail server over the POP3 or IMAP4 protocol, downloads the message, and after that can view it in the email client interface.
The main differences between the POP3 and IMAP4 protocols are in the following facts:
- The POP3 protocol downloads an entire email message completely to the user's computer. This does not ensure reverse synchronization. All the actions performed with a message in the client-side application (e.g., reading, moving) are not transferred to the server and cannot be displayed in other email clients.
- The IMAP4 protocol allows to work with the mail server without downloading the entire message, but downloading the display of the status for the email messages on the server. A user can view email headers only and selectively download the messages he want to read by clicking on the necessary header. This protocol ensures reverse synchronization.
Particulars of the ONLYOFFICE Mail implementation
ONLYOFFICE Mail includes the following main components:
- Mail Aggregator - a service that collects email messages from other mailboxes.
The following components are also used to ensure the mail aggregator operation:
- Own email storage,
- The email storage API,
- HTTP server that processes the requests to this API. It is also responsible for sending emails.
In the user interface with a set of standard folders, you can connect existing mailboxes specifying your login, password and settings for connection to a mail server. The mail aggregator will download email messages from the connected mailboxes into the storage over the protocol used for retrieving email (POP3 or IMAP4) that is specified in the connection settings. You will be able to view the received messages and send emails from any of the connected mailboxes.
The mail aggregator always works with a delay. If there are a lot of users on your portal, a number of settings can be used to ensure that email messages for all user are delivered in a certain time period. First the aggregator collects new messages, and then collects all others. It's also possible to collect messages only for the last 30 days, or give priority to active portal users.
None of the actions performed in our client are transferred to the source server, with the only exception: a sent message is placed to the "Sent" folder on the server.
- Mail Server - a set of software products that allows to send and receive email messages from the ONLYOFFICE Mail interface using own domain names.
The following components are also used to ensure the mail server operation:
- MailServer API - a set of functions for connecting own domain names, creating and setting up mailboxes, aliases and mail groups.
- MailServer WebUI - the Administration page used for the interaction with the MailServer API.
- Mail Aggregator, which is described above.
The main differences between ONLYOFFICE Mail and other email programs are in the following facts:
- ONLYOFFICE Mail Server supports the SMTP, IMAP and POP3 protocols, but email messages are sent using HTTP server.
- ONLYOFFICE Mail Server does not have own email client. The Mail Aggregator is used for working with ONLYOFFICE Mail Server, like for the interaction with any other third-party mail server.
This results in some restrictions. For example, it's not possible to implement full-fledged operation via the IMAP protocol.
If a mail server has own email client, there are no restrictions on the number of connections from the same IP address between the client-side and server-side applications, while such restrictions always exist when working with third-party clients.
As we work with ONLYOFFICE Mail Server using the mail aggregator rather than own email client, this restriction may work if there are a lot of users on the portal, because all the users' mailboxes are on the same IP address.